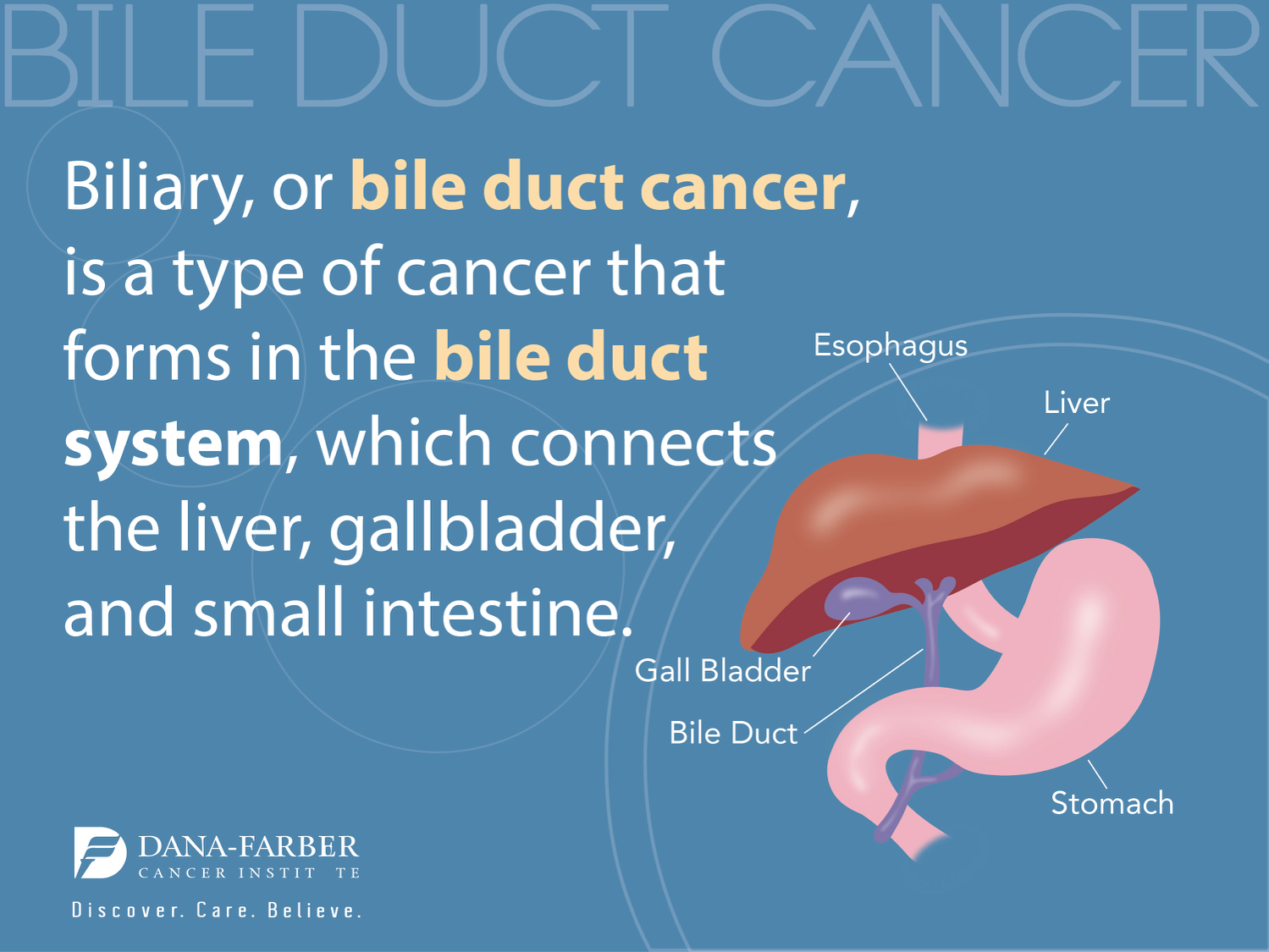
Bile imbalance liver cancer is an emerging area of research that highlights the critical link between bile acids produced by the liver and the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies suggest that an imbalance in bile acid levels can lead to significant liver damage, inflammation, and ultimately cancer. This highlights the urgent need for innovative liver cancer treatment options that target the molecular mechanisms underlying these disturbances. By understanding the role of key factors like the YAP signaling pathway and the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), researchers are uncovering potential therapeutic avenues to restore bile balance and mitigate the risks of liver cancer. With new insights and interventions on the horizon, the fight against liver cancer continues to evolve, offering hope for affected individuals.
The connection between bile acid dysregulation and liver malignancies, often referred to as bile acid imbalance-related liver cancer, is garnering increased attention in medical research. Bile acids, essential for fat digestion, also serve as signaling molecules that profoundly influence metabolic functions. Disruptions in their homeostasis can lead to liver injury and promote conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma, the predominant type of liver cancer. Investigations into molecular mechanisms like the FXR and YAP pathways are crucial in understanding these processes, providing promising targets for novel therapeutic strategies. As advances unfold in this complex field, the potential for effective liver cancer treatments becomes increasingly attainable.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Connection to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance has emerged as a significant contributing factor to the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, traditionally known for their ability to aid in fat digestion, also possess a hormone-like function that influences various metabolic processes within the liver. According to recent research, disruptions in bile acid production and regulation can lead to inflammatory conditions and ultimately promote cancerous growth. This highlights the need for ongoing research into how the balance of bile acids is intricately linked not just to liver health, but also to the onset of severe conditions such as liver cancer.
Recent studies have identified a critical molecular switch that may play a pivotal role in the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer. By focusing on the mechanisms that regulate bile acid metabolism, scientists have discovered that the activation of the YAP signaling pathway interferes with the function of the FXR receptor, a crucial component for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. This interference can lead to an accumulation of bile acids in the liver, fostering an environment conducive to fibrosis, inflammation, and ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma.
The Role of the YAP Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancer Development
The YAP signaling pathway is an essential regulator in many cellular processes, including cell growth and division, making it a focal point in liver cancer research. Studies reveal that when activated, YAP can paradoxically suppress the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a critical player in maintaining normal bile acid levels. This suppression not only disrupts bile acid metabolism but also leads to liver damage that can promote the progression of liver cancer. This indicates that therapeutic strategies targeting YAP could potentially mitigate the risk of developing HCC.
Understanding the intricate relationship between YAP signaling and bile acid regulation opens new avenues for potential liver cancer treatments. By inhibiting YAP or enhancing FXR function, researchers aim to restore the balance of bile acids, reduce liver damage, and slow cancer progression. This research could lead to the development of pharmacological interventions designed to stimulate FXR activity, representing a promising direction in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment.
Therapeutic Implications of Bile Acid Regulation in Liver Cancer
Therapeutic advancements derived from the understanding of bile acid regulation are crucial in the fight against liver cancer. Since the FXR receptor plays a pivotal role in bile acid homeostasis, pharmacological agents that can enhance FXR function could serve as effective treatments for patients with liver anomalies related to bile imbalance. Clinicians are closely monitoring these developments as they represent a potential shift in how liver cancer, particularly when linked to dysregulated bile, is treated and managed.
Additionally, promoting bile acid excretion through dietary modifications or pharmacological means could provide another layer of protective mechanisms against liver damage and cancer progression. By incorporating lifestyle changes that support liver health, patients may experience not only improved liver function but potentially a lower risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. The interconnectedness of bile acids, FXR, and liver cancer treatment underscores the significance of ongoing research and innovative therapies.
Key Molecular Switches for Potential Liver Cancer Treatment
The identification of key molecular switches involved in bile acid metabolism is reshaping the landscape of liver cancer treatment options. As researchers delve deeper into the roles of YAP and FXR, they are uncovering novel therapeutic targets that could revolutionize how hepatocellular carcinoma is approached. The potential to modify these signaling pathways could lead to the development of targeted therapies that not only address cancerous cells directly but also rectify the underlying metabolic imbalances.
This forward-thinking strategy is supported by findings that indicate enhancing FXR activity can reverse liver damage and impede cancer progression. By strategically focusing on the molecular mechanisms influenced by YAP and the degradation of bile acids, an intricate yet powerful approach to liver cancer treatment may emerge, offering hope to patients battling this daunting disease.
The Importance of Bile Acids in Liver Health
Bile acids are more than just components of bile; they serve critical roles in hepatic physiology and overall health. Beyond facilitating lipid digestion, bile acids act as signaling molecules, influencing metabolic regulation throughout the liver and beyond. Their balance is crucial, as dysregulation can lead to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and, ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the multifaceted functions of bile acids highlights their importance in liver health and disease prevention.
Furthermore, imbalances in bile acids are increasingly recognized as potential biomarkers for liver conditions. Research indicates that analyzing bile acid profiles can provide insights into liver function, disease progression, and therapeutic responsiveness in patients with liver cancer. By focusing on bile acids not just as a digestive aid, but as critical players in liver pathology, we pave the way for innovative diagnostics and treatments.
Investigating FXR: A Promising Target for Liver Cancer Treatment
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is emerging as a promising target in liver cancer treatment due to its vital role in maintaining bile acid balance and liver homeostasis. As research highlights the detrimental effects of YAP activation on FXR function, the potential for FXR-targeted therapies becomes clear. By restoring FXR activity, it may be possible to alleviate the overproduction of bile acids and mitigate the inflammatory processes that contribute to liver cancer.
Moreover, FXR’s influence extends beyond bile acid regulation. It also plays a role in glucose and lipid metabolism, which are intricately linked to liver health. By harnessing the therapeutic potential of FXR, researchers envision a multifaceted approach to treating liver cancer that simultaneously addresses metabolic disturbances and cancerous growth, ultimately leading to better outcomes for patients.
The Implications of Bile Acid Dysregulation in Liver Disease
Dysregulated bile acid homeostasis is increasingly correlated with various liver diseases, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. When bile acids accumulate due to impaired secretion or metabolism, they can cause inflammatory responses, leading to cellular damage and promoting tumorigenesis. Understanding the complex interplay between bile acid dysregulation and liver pathology is crucial as it can guide preventative measures and treatment strategies.
Moreover, recognizing that bile acid dysregulation can serve as a therapeutic target provides a pathway for novel interventions to treat liver disease. As research continues to unveil the mechanisms by which bile acids influence liver health, the potential for developing therapies that restore bile acid balance and mitigate liver damage becomes a plausible reality, highlighting the need for continued exploration in this area.
Research Directions on Bile Acids and Liver Cancer Correlation
Future research directions focusing on the correlation between bile acids and liver cancer could yield groundbreaking findings. By exploring the trajectory of bile acid metabolism and its regulatory pathways, scientists can uncover the underlying mechanisms that precipitate liver disease. This research could potentially lead to new diagnostic markers and therapeutic approaches, emphasizing the need for an integrative understanding of liver biology and cancer.
In addition, studying the interactions between bile acids, cell signaling pathways, and environmental factors may reveal important insights into the prevention and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Collaborative efforts across disciplines will be essential in bridging the gap between basic science and clinical applications, aiming to translate findings into effective strategies for combating liver cancer rooted in bile metabolism imbalances.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Liver Health and Prevent Cancer
Incorporating lifestyle modifications can significantly influence bile acid metabolism and overall liver health, potentially reducing the risk of liver cancer. Dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake, decreasing saturated fats, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, can enhance bile production and promote bile acid homeostasis. Regular physical activity also contributes to maintaining optimal metabolic function and liver health.
Additionally, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy weight are critical factors in supporting liver function. By adopting a comprehensive approach that encompasses dietary, physical, and behavioral factors, individuals may bolster their liver health and lower the chances of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, thus empowering preventive health measures against liver diseases linked to bile imbalance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance, specifically the disruption in bile acid regulation, is linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When bile acid production is not properly regulated, it can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are precursors to cancer. Key studies have shown that an imbalance can trigger pathways involved in tumor formation and progression.
How does YAP signaling contribute to bile imbalance and liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) signaling plays a significant role in bile imbalance and liver cancer. It has been found that YAP can inhibit the function of FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), a critical bile acid sensor that regulates bile acid metabolism. This inhibition leads to an overproduction of bile acids, contributing to liver inflammation and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Can liver cancer treatment be improved by targeting bile acids?
Yes, targeting bile acids presents a promising avenue for liver cancer treatment. Research indicates that enhancing the function of FXR or promoting the excretion of bile acids may block the detrimental effects of YAP and reduce liver damage, potentially slowing cancer progression and providing new pharmacological interventions.
What role do bile acids play in liver health and cancer development?
Bile acids are essential for digesting fats and have a hormone-like function that regulates various metabolic processes in the liver. Disruption in bile acid homeostasis due to factors like YAP signaling can lead to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), highlighting the importance of bile acids in maintaining liver health.
What molecular mechanisms are involved in bile acid metabolism related to liver cancer?
The study of bile acid metabolism related to liver cancer involves critical molecular mechanisms, including the regulation by FXR and the interference from YAP signaling. When YAP inhibits FXR, it leads to an imbalance in bile acids, precipitating liver damage and contributing to HCC development. Understanding these mechanisms paves the way for targeted treatments.
How can enhancing FXR function help with liver cancer prevention?
Enhancing FXR function can help prevent liver cancer by restoring the balance of bile acids. By reversing the inhibitory effect of YAP, it promotes proper bile acid metabolism and reduces liver inflammation and damage, which are risk factors for developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
What future research is needed regarding bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Future research should focus on developing pharmacological agents that can activate FXR or inhibit YAP signaling to effectively regulate bile acid metabolism. Additionally, more studies are needed to explore the complex interplay between bile acids, liver health, and cancer development to identify novel therapeutic strategies.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Imbalances in bile acids produced by the liver can lead to liver diseases including liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch | A molecular switch, YAP, regulates bile acid metabolism and plays a role in tumor formation. |
| Role of FXR | FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) is crucial for maintaining bile acid balance; YAP inhibits its function. |
| Potential Treatment Strategies | Enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion could be potential therapeutic interventions. |
| Research Implications | The study could lead to pharmacological solutions targeting FXR for liver cancer treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is an emerging area of research that highlights the significant role that bile acids play in liver health. This study underscores the intricate relationship between bile production, cellular metabolism, and liver disease progression. Understanding how bile acid regulation can lead to liver cancer provides insights into new treatment opportunities that might improve outcomes for patients.